Component Conveyor Transport
Inline Operations
Inline operations require a conveyor to move product from upstream, through the system, to a downstream system. Communications between a dispense system and the upstream and downstream systems is done via SMEMA. SMEMA is a communications standard for systems to signify when it is acceptable to transport a product.
Modes of running inline are:
- Continuous - Products are brought into the system, processed, and transported out of the system. This is considered a normal mode of operation.
- Pass Through - In some instances, there may NOT be a dispensing process to be done on the product. The system passes product through the system without processing based on the SMEMA protocol.
Product is transported on either 3 mm or 5 mm anti-static belts. Standard belts are flat. Additional belt sizes and styles are available for applications that require non-standard belts.
Support of the product during processing is done with a lifter plate. Lifter plates lift the product from the conveyor belt, clamping the side edges and top to a registered flat surface. Lifting the product from the belt ensures that the product will be flat and remain undisturbed by conveyor belt movement.
Lifter Plates
Lifter plates comes in two primary sizes: 14.1" x 12" and 10" x 10". The larger plate, the standard size, is made from steel to support magnetic support pins. Mounting holes in the plate accommodate custom fixtures. The large size enables it to handle the full scope of the MAX Series work area. Since the plate is made from steel, it can hold magnetic support pins that may be freely moved around the worktable. Support pins come in two types: spring-loaded and vacuum. Spring-loaded pins contact a product, lift it from the conveyor with up to 1" of travel, and clamp it to supports on the topside of the conveyor. The pins are spring-loaded to comply to product shape. For applications requiring a greater degree of flatness, vacuum pins may be used. Vacuum pins contact the product, then pull it flat to the surface of the vacuum pin.
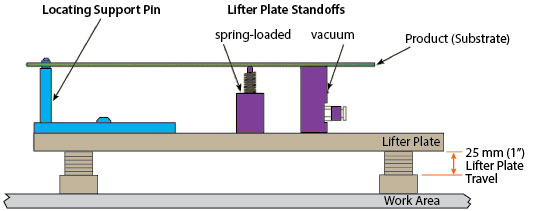
The smaller plate is used when a compact design is desired and is typically set to a specific fixture or size of product. In this case, the lifter does not accommodate the full work area and is limited in the number of fixtures the plate can accommodate.
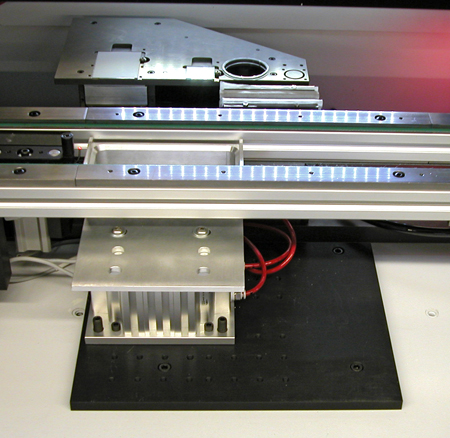

Work Area Sensors
During transport, the system keeps track of where the product should be. The work area sensor detects the board edge when it reaches the processing position. If the sensor does not trigger within the allowed amount of time, an operator is notified to inspect the transport system. When transport of a product through the system is completed, the stop pin recedes, allowing the product to move to the downstream system. An additional sensor, located beyond the stop pin, must be cleared before the stop pin will lift. This ensures that the product will not get stuck and it prevents the stop pin from damaging the product.
Auto Width Adjust
Auto Width Adjust is available on all conveyors. Auto width adjust automatically adjusts the width of the conveyor when a program starts. This features minimizes operator interaction and helps to ensure the system is set up correctly.
Dual Speed Conveyor
An optimized dual speed conveyor enhances product transport. Dual speed transport allows products to be transferred at a high rate of speed over the long distance between stations, slowing just before the product reaches the board stop. By reducing the speed before reaching the board stop, the substrate is gently stopped, avoiding shock to the product being transported, thus preventing the loss of product before it's even processed.


